Introduction
Welcome to the world of self-driving cars, where technology meets transportation like never before. In this blog post, we will explore the fascinating realm of autonomous vehicles, shedding light on how they function, the underlying technologies, safety concerns, the current state of development, legislative hurdles, and when we can realistically expect to see self-driving cars becoming a common sight on our roads.
Join us on this journey as we demystify the science behind self-driving cars and envision the future of automotive travel.
How Self-Driving Cars Function

Self-driving cars, also known as autonomous vehicles, rely on cutting-edge technology to navigate and operate on the roads without human intervention. Understanding how these vehicles function is essential to appreciate the revolution they are bringing to the world of transportation.
Here’s an overview of the key components and processes that enable self-driving cars to operate:
Sensor Systems
Sensor systems are the eyes and ears of self-driving cars. These vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors. These sensors continuously scan the car’s surroundings, collecting data on nearby objects, pedestrians, road markings, and traffic signals.
Mapping and Localization
Accurate maps and precise vehicle localization are critical for autonomous driving. Self-driving cars use high-definition maps that include detailed information about roads, lanes, and landmarks. Simultaneously, GPS and onboard sensors help the vehicle determine its exact position on the map in real-time.
Perception and Decision-Making
The onboard computer system processes the data collected from sensors and combines it with the map and localization information. Advanced machine learning algorithms analyze this data to identify and classify objects, predict their behavior, and make informed decisions. For example, the car can recognize a pedestrian at a crosswalk and decide to stop.
Control Systems
Once the car has made a decision, it uses control systems to execute the action. This includes steering, accelerating, and braking. Modern self-driving cars are equipped with drive-by-wire systems, which allow electronic control over these functions.
Redundancy and Safety Measures
Ensuring safety is paramount in autonomous driving. Self-driving cars often incorporate redundant systems and backup mechanisms to handle unexpected situations. For instance, if a sensor fails, the car must have backup sensors or alternative strategies to maintain safe operation.
Here’s a simple table summarizing the key components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensor Systems | Collect data on the car’s surroundings |
| Mapping and Localization | Provide high-definition maps and real-time vehicle positioning |
| Perception and Decision-Making | Process sensor data, make decisions, and predict actions |
| Control Systems | Execute driving actions like steering and braking |
| Redundancy and Safety Measures | Ensure safe operation and handle failures |
Self-driving cars represent a remarkable fusion of artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and automotive engineering. As these technologies continue to advance, we can expect autonomous vehicles to play a more significant role in the future of transportation.
The Key Technologies Behind Self-Driving Cars

Self-driving cars are a marvel of modern technology, relying on a combination of cutting-edge innovations to operate safely and efficiently. Here, we delve into the key technologies that make autonomous vehicles a reality:
Sensor Technology
At the heart of self-driving cars are sophisticated sensor systems. These vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors, including:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): LiDAR sensors use laser beams to create detailed 3D maps of the car’s surroundings, allowing it to detect objects and obstacles with high precision.
- Radar: Radar sensors use radio waves to detect objects, measure their speed, and provide critical data for collision avoidance.
- Cameras: Multiple cameras capture images and video to identify lane markings, traffic signs, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors use sound waves to detect nearby objects, aiding in parking and low-speed maneuvering.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Self-driving cars rely heavily on artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These algorithms analyze data from sensors in real-time, identifying objects, predicting their behavior, and making driving decisions. Reinforcement learning allows the car to adapt and improve its driving skills over time.
High-Definition Mapping
Accurate maps play a crucial role in autonomous driving. High-definition maps provide detailed information about road geometry, lane markings, traffic signs, and even the curvature of the road. Self-driving cars use these maps for precise localization and as a reference for navigation.
Connectivity
Self-driving cars often rely on connectivity to communicate with other vehicles (V2V) and infrastructure (V2I). This enables the sharing of data about traffic conditions, road closures, and potential hazards, enhancing overall safety and efficiency.
Computing Power
The onboard computer systems in self-driving cars are incredibly powerful. They process vast amounts of data from sensors and run complex AI algorithms in real-time. These computers must be reliable and have redundancy to ensure safety.
Safety Systems
Ensuring the safety of passengers and pedestrians is a top priority. Self-driving cars incorporate numerous safety systems, including redundant sensors, backup controls, and fail-safe mechanisms. In the event of a system failure or emergency, the car can take appropriate action to prevent accidents.
Here’s a simplified table summarizing these key technologies:
| Technology | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensor Technology | Collect data on the car’s surroundings |
| Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning | Process sensor data, make driving decisions |
| High-Definition Mapping | Provide detailed maps for navigation and localization |
| Connectivity | Enable communication with other vehicles and infrastructure |
| Computing Power | Process and analyze data, run AI algorithms |
| Safety Systems | Ensure safe operation and handle emergencies |
The convergence of these technologies is driving the rapid development of self-driving cars, offering the potential for safer, more efficient, and convenient transportation in the near future.
Challenges and Safety Concerns
While self-driving cars hold the promise of transforming transportation, they also face significant challenges and safety concerns that need to be addressed before they become a ubiquitous sight on our roads. Here, we explore some of the most pressing issues:
1. Technical Challenges
Complex and Unpredictable Environments: Self-driving cars must navigate through a wide range of environments, from busy city streets to rural roads, and handle various weather conditions. Ensuring their ability to react to unpredictable situations is a formidable technical challenge.
Interacting with Human-Driven Vehicles: Self-driving cars need to safely share the road with human drivers who may not always follow predictable patterns or obey traffic rules.
2. Safety Concerns
Accident Liability: Determining liability in the event of an accident involving a self-driving car raises complex legal and ethical questions. Is it the responsibility of the vehicle owner, the manufacturer, or the software developer?
Cybersecurity Risks: Autonomous vehicles are vulnerable to hacking, which could lead to unauthorized control, data theft, or malicious interference. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is crucial.
Data Privacy: Self-driving cars collect vast amounts of data about their surroundings and passengers. Protecting this data from misuse and ensuring privacy is a growing concern.
3. Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
Regulatory Frameworks: Developing comprehensive regulations for self-driving cars is a complex process. Governments and regulatory bodies must balance innovation with safety and establish clear guidelines for testing and deployment.
International Standards: Coordinating international standards and regulations for self-driving cars is essential to ensure compatibility and safety on a global scale.
4. Public Acceptance and Education
Public Trust: Gaining public trust in self-driving technology is an ongoing challenge. Many people remain skeptical about the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles.
Education and Awareness: Public education campaigns are needed to inform people about the capabilities and limitations of self-driving cars and their potential benefits for society.
Addressing these challenges and safety concerns requires collaboration among governments, technology companies, and the automotive industry. While self-driving cars offer exciting possibilities, their successful integration into our daily lives depends on addressing these issues with diligence and care.
The Current State of Self-Driving Car Development
The development of self-driving cars has made significant strides in recent years, with numerous companies and research institutions actively working on bringing autonomous vehicles to the market. Here’s a snapshot of the current state of self-driving car development:
1. Industry Players
Several prominent companies are at the forefront of self-driving car technology:
- Tesla: Tesla’s Autopilot system offers advanced driver assistance features, although it falls short of full autonomy. The company continues to develop and test self-driving capabilities.
- Waymo: A subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. (Google’s parent company), Waymo is a leader in autonomous driving technology. They’ve launched a commercial ride-hailing service called Waymo One in select areas.
- General Motors (GM): GM’s subsidiary, Cruise, is working on self-driving technology and aims to deploy autonomous ride-sharing vehicles in the near future.
- Uber: Uber’s Advanced Technologies Group (ATG) is actively testing autonomous vehicles and is partnering with other companies to advance self-driving technology.
2. Testing and Pilots
Companies are conducting extensive testing and pilot programs to refine self-driving technology:
- Self-driving cars are being tested on public roads in various cities worldwide, including San Francisco, Phoenix, and Pittsburgh.
- Companies like Waymo and Cruise are running autonomous ride-hailing services with safety drivers in select areas.
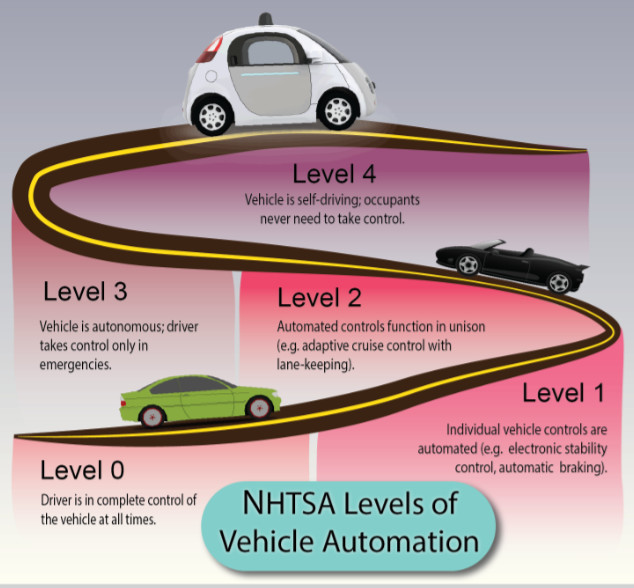
3. Levels of Autonomy
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines levels of automation from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). Most self-driving cars are currently at Level 2 or 3, where they can handle some driving tasks but still require human supervision.
4. Regulatory Progress
Regulations governing self-driving cars are evolving to accommodate this emerging technology:
- The U.S. Department of Transportation has issued guidelines for autonomous vehicles, and some states have enacted legislation to facilitate testing and deployment.
- International organizations are also working on harmonizing standards to enable global deployment.
5. Public Perception
Public perception of self-driving cars remains mixed, with concerns about safety and trust in autonomous technology. Companies are working to address these concerns through education and transparency.
It’s important to note that while significant progress has been made, the road to fully autonomous vehicles is still long and complex. Overcoming technical challenges, ensuring safety, and gaining regulatory approval are ongoing efforts that will shape the future of self-driving cars.
As technology continues to advance and industry players refine their approaches, we can expect to see self-driving cars playing a more significant role in our transportation landscape in the years to come.
Legislation and Regulations
As self-driving cars inch closer to becoming a reality on our roads, the need for comprehensive legislation and regulations to govern their use and deployment has become increasingly apparent. Here, we delve into the evolving landscape of legislation and regulations surrounding autonomous vehicles:
1. Federal Regulations
The United States is among the countries at the forefront of establishing federal regulations for self-driving cars:
- NHTSA Guidelines: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has issued guidelines outlining the federal government’s approach to autonomous vehicle regulation. These guidelines provide a framework for manufacturers to test and deploy self-driving cars safely.
- AV START Act: The “American Vision for Safer Transportation through Advancement of Revolutionary Technologies (AV START) Act” is proposed legislation aimed at establishing a national framework for the regulation of autonomous vehicles. While it has not yet become law, it highlights the importance of federal involvement in regulating self-driving cars.
2. State-Level Regulations
Many U.S. states have taken the initiative to create their own regulations and legislation related to self-driving cars:
- Testing and Deployment: States like California, Arizona, and Michigan have allowed companies to test self-driving vehicles on public roads under specific conditions. Some states have also passed laws to allow for the deployment of autonomous vehicles for commercial purposes.
- Insurance and Liability: Some states have addressed insurance and liability issues by establishing rules for how insurance companies handle claims involving self-driving cars.
3. International Regulations
Self-driving cars are a global phenomenon, and international organizations are working to create harmonized regulations:
- UNECE Regulations: The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) is developing regulations for the deployment of automated vehicles. These regulations aim to provide a global framework for the safe operation of self-driving cars.
- ISO Standards: The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is working on international standards related to autonomous vehicles, covering aspects like safety, communication, and testing.
4. Safety and Data Privacy
Regulations not only focus on vehicle safety but also on data privacy and cybersecurity:
- Data Protection: Regulations may require manufacturers to implement robust data protection measures to safeguard the privacy of passengers and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data collected by self-driving cars.
- Cybersecurity: Laws and regulations address the need for strong cybersecurity practices to protect self-driving vehicles from hacking and cyber threats.
As the technology matures and self-driving cars become more prevalent, the regulatory landscape will continue to evolve. Governments and international organizations are working collaboratively to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring the safety and security of autonomous vehicles on our roads.
It’s crucial for industry stakeholders, policymakers, and the public to stay informed about these evolving regulations to navigate the path toward a future with self-driving cars safely integrated into our transportation systems.
When Can We Expect Self-Driving Cars on the Road?
The timeline for the widespread adoption of self-driving cars is a subject of great interest and speculation. While significant progress has been made in self-driving technology, several factors influence when we can expect these autonomous vehicles to become a common sight on our roads:
1. Development Stages
Self-driving car development typically progresses through various stages, from research and development to testing and limited deployment:
- Research and Development: Companies invest years in researching and developing the technology required for autonomous driving.
- Testing: Rigorous testing on public roads is a critical phase to refine and validate self-driving systems.
- Limited Deployment: Companies often start with limited deployments, such as ride-hailing services in specific cities, to gain real-world experience and collect data.
2. Technological Challenges
Addressing technical challenges remains a significant factor in determining the timeline for self-driving cars:
- Complex Environments: Ensuring self-driving cars can handle diverse and complex driving environments, including inclement weather and challenging traffic scenarios, is an ongoing challenge.
- Safety and Reliability: Achieving a level of safety and reliability that meets or exceeds human drivers is crucial before widespread deployment.
3. Regulatory Framework
Regulatory approval and legislation play a pivotal role in the deployment of self-driving cars:
- Federal and State Regulations: Clear and consistent regulations at both federal and state levels are essential to provide a legal framework for self-driving car operations.
- Safety Certification: Autonomous vehicle manufacturers must meet safety certification standards to ensure public safety.
4. Public Acceptance
Public perception and trust in self-driving technology are crucial factors:
- Educating the Public: Efforts to educate the public about the safety and benefits of autonomous vehicles can help build trust.
- Real-World Experience: Positive experiences with self-driving cars during limited deployments can boost public confidence.
5. Business Models
The business models adopted by companies developing self-driving cars can influence deployment timelines:
- Ride-Hailing Services: Companies like Waymo and Uber are actively working on autonomous ride-hailing services, which could see broader adoption sooner.
- Consumer Ownership: The availability of self-driving cars for consumer ownership may take more time to materialize due to various factors, including cost and infrastructure.
While we are witnessing the gradual introduction of self-driving technology in select areas, achieving full autonomy across all driving scenarios and widespread adoption will take time. Predicting an exact timeline remains challenging, but experts suggest that self-driving cars may become more common on our roads within the next decade, with the pace of adoption varying by region and use case.
Ultimately, the timeline for self-driving cars hinges on a delicate balance between technological advancements, regulatory developments, public acceptance, and successful business models.
FAQ
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about self-driving cars:
Q: What is a self-driving car?
A: A self-driving car, also known as an autonomous vehicle, is a vehicle that can operate and navigate without human intervention. It uses various sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence algorithms to sense its surroundings and make driving decisions.
Q: How do self-driving cars work?
A: Self-driving cars use sensors and cameras to collect data about their environment. This data is processed by onboard computers, which use machine learning algorithms to make driving decisions, such as steering, accelerating, and braking. High-definition maps and GPS help with navigation.
Q: Are self-driving cars safe?
A: Safety is a top priority in self-driving car development. While accidents can still occur, autonomous vehicles have the potential to reduce human error, which is a leading cause of accidents. Extensive testing and safety features are in place to minimize risks.
Q: When will self-driving cars be available to the public?
A: The timeline for public availability of self-driving cars varies by region and use case. Some companies are already testing autonomous ride-hailing services in select cities, but widespread consumer ownership may take several years to become a reality.
Q: What are the benefits of self-driving cars?
A: Self-driving cars have the potential to improve road safety, reduce traffic congestion, and provide greater mobility for people who cannot drive, such as the elderly and disabled. They may also lead to more efficient use of transportation resources.
Q: What are the challenges facing self-driving cars?
A: Challenges include technical hurdles related to complex driving environments, regulatory frameworks, public acceptance, and addressing issues like cybersecurity and data privacy.
Q: Will self-driving cars eliminate the need for human drivers?
A: While self-driving technology may reduce the need for human drivers in some scenarios, such as long-haul trucking and ride-hailing services, human drivers will likely still be required for many years, especially for complex driving situations.
These FAQs provide a basic understanding of self-driving cars, their benefits, challenges, and the timeline for their adoption. As the technology continues to evolve, more questions and answers will emerge in this rapidly advancing field.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the advent of self-driving cars represents a significant transformation in the world of transportation. While we’ve made remarkable progress in developing autonomous vehicles, there are still challenges to overcome, both technical and regulatory, before they become a common sight on our roads.
Self-driving cars have the potential to revolutionize road safety, reduce traffic congestion, and provide increased mobility for various segments of the population. However, achieving the level of safety and reliability required for widespread adoption remains a top priority for developers and regulators.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to accommodate this emerging technology, with both federal and state-level regulations in place to guide the testing and deployment of self-driving cars. International efforts are also underway to establish global standards for autonomous vehicles.
Public perception and trust in self-driving technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of autonomous vehicles. Continued education and transparency efforts are essential to build confidence in these advanced systems.
While the timeline for widespread adoption remains uncertain, we can expect to see self-driving cars playing a more prominent role in our transportation ecosystem in the coming years. The pace of adoption may vary by region and use case, but the potential benefits they offer are undeniable.
As self-driving technology continues to advance and regulatory frameworks become more established, we look forward to a future where autonomous vehicles coexist with human-driven cars, contributing to safer and more efficient transportation for all.
Stay tuned for further developments in the exciting journey toward the widespread adoption of self-driving cars.